| SKU | Image | Name | Price | Quantities | Buy |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
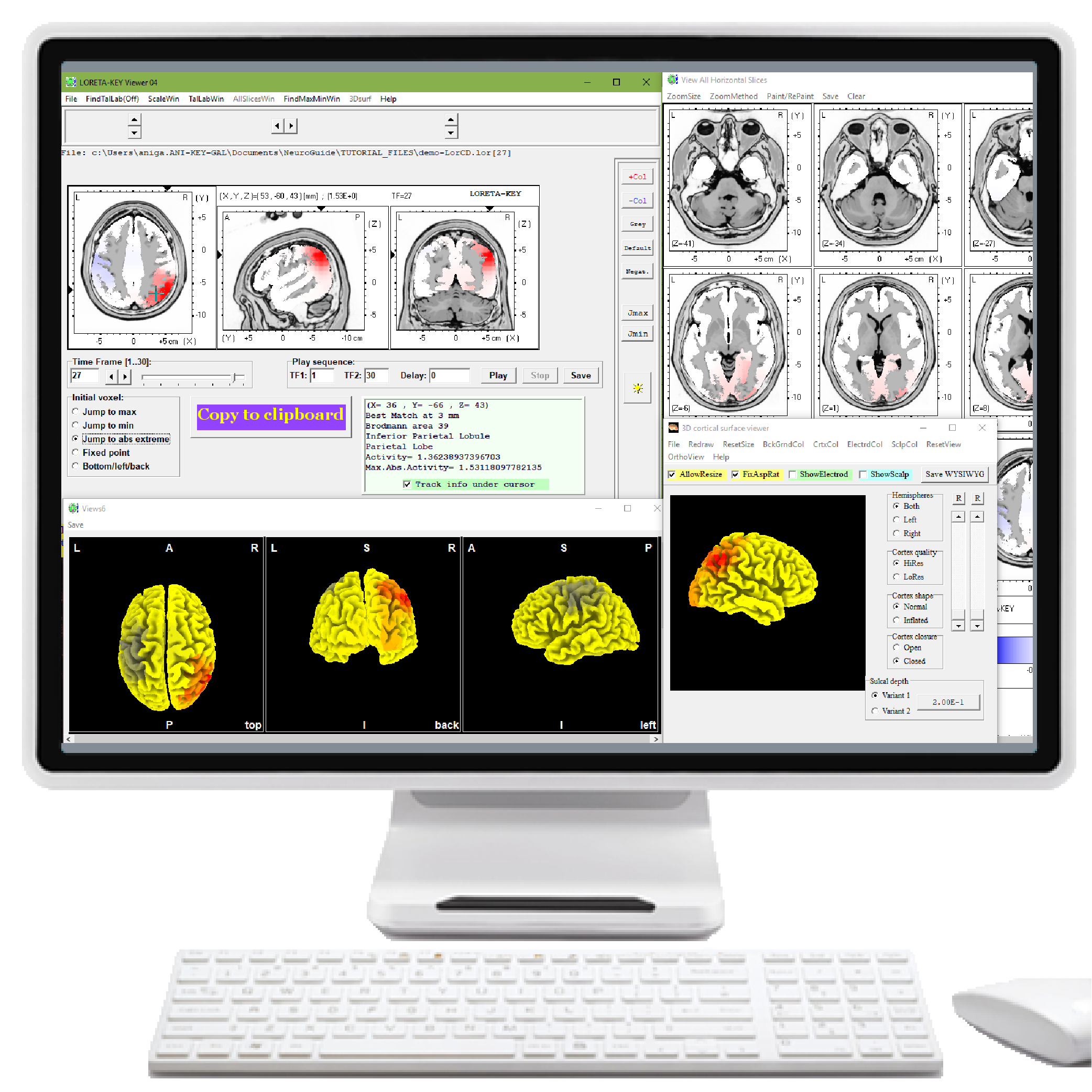
| LOR | LORETA Current Density Normative Database | $1,200.00 | |||
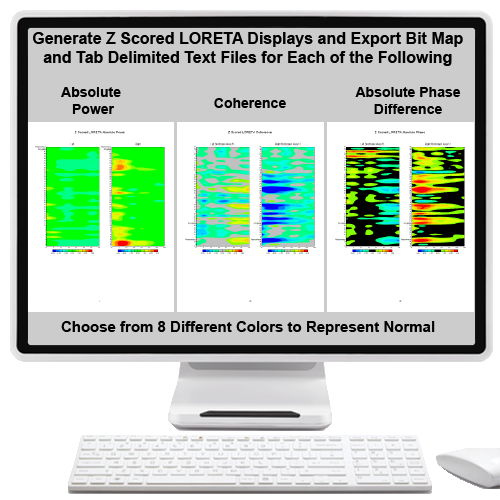
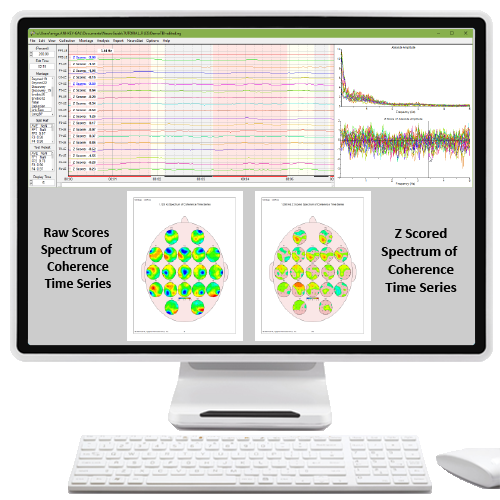
| LCP | LORETA Coherence and Phase Differences | $1,200.00 | |||
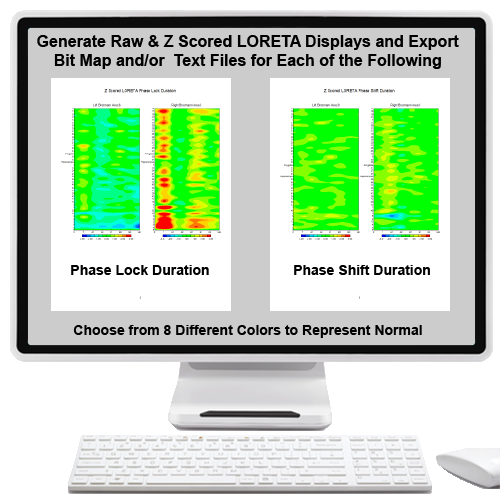
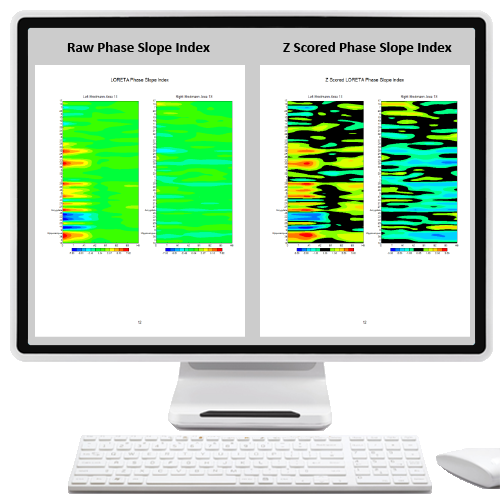
| LPR | LORETA Phase Reset | $1,200.00 | |||
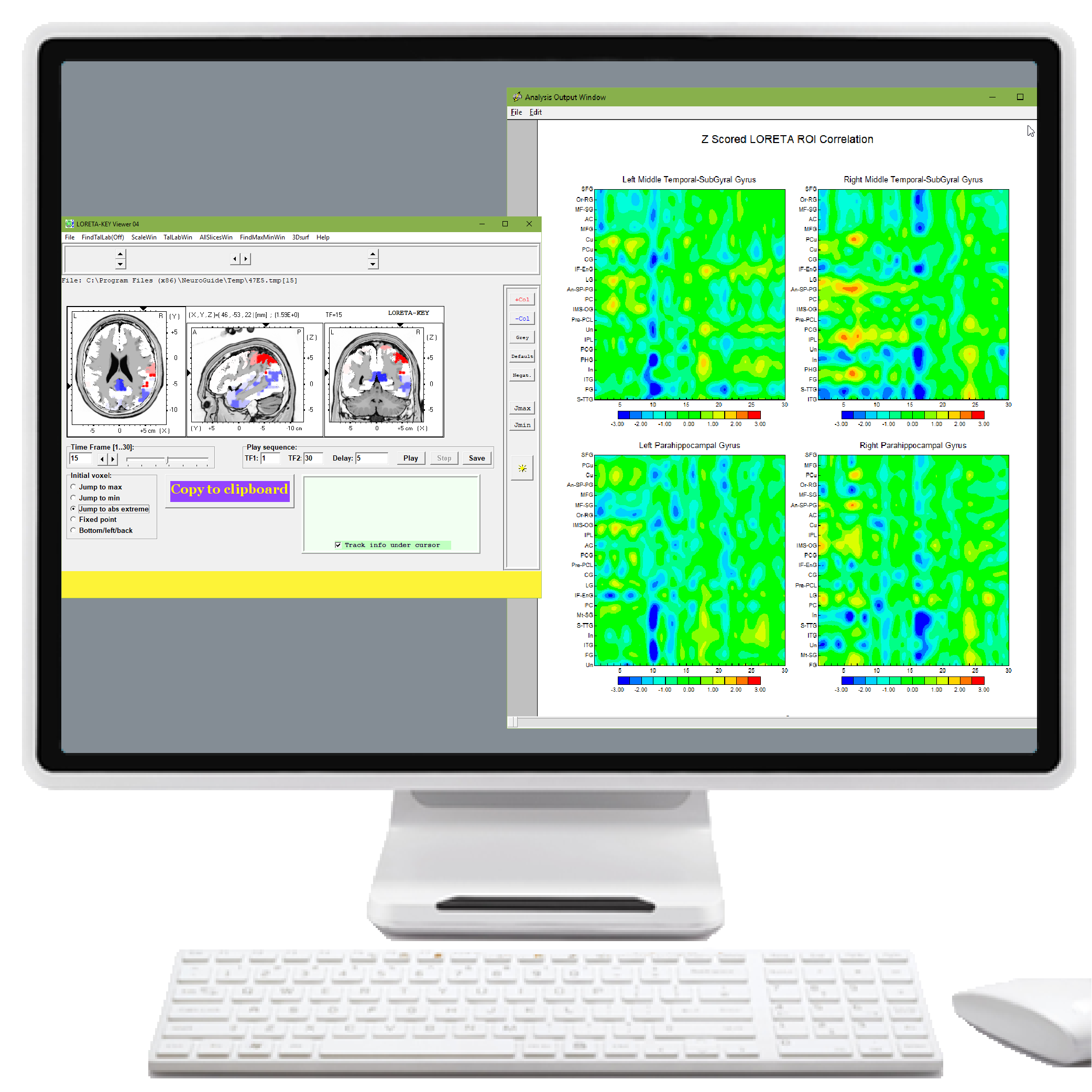
| SC | LORETA Source Correlation | $1,200.00 | |||
| ECL | LORETA Effective Connectivity | $1,200.00 | |||
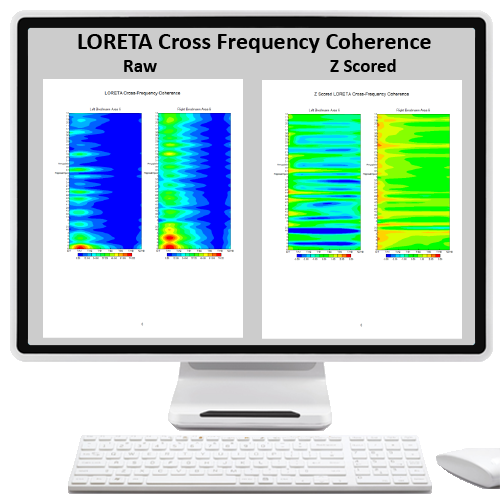
| CFC-L | LORETA Cross-Frequency Coherence | $1,200.00 | |||
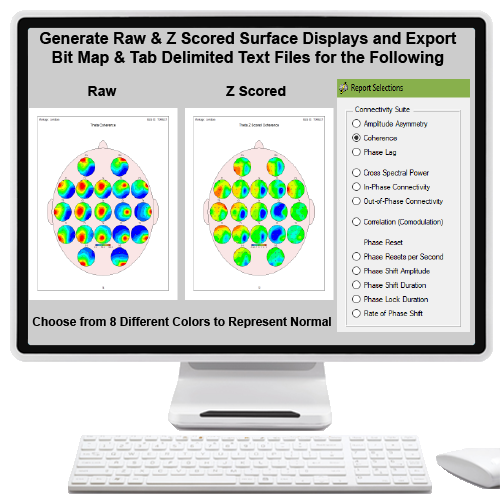
| CS | Connectivity Suite | $700.00 | |||
| BS | Dynamic Bi-Spectral Analyses | $700.00 | |||
| ECS | Surface Effective Connectivity | $700.00 | |||
| CFP-S | Surface Cross-Frequency Power | $700.00 | |||
| CFC-S | Surface Cross-Frequency Coherence | $700.00 | |||
| CFPA-S | Surface Cross-Frequency Phase Amplitude | $700.00 |